Ligures
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2021) |
Ligurians Ligures | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1200 BC (iron age in Italy (geographical region))–AD 63 | |||||||
 Ancient Liguria corresponds almost entirely to present-day Liguria. | |||||||
| Status | City-states[1][2] | ||||||
| Common languages | Ligurian (ancient language) | ||||||
| Religion | Ligurian[3] | ||||||
| Government | Chiefdom | ||||||
| Historical era | Liguria, Italy | ||||||
• Established | 1200 BC (iron age in Italy (geographical region)) | ||||||
| AD 63 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Today part of |
| ||||||
| History of Italy |
|---|
 |
|
|

The Ligures (singular Ligur; Italian: liguri; English: Ligurians) were an ancient people after whom Liguria, a region of present-day north-western Italy, is named.[5]


Ancient Liguria corresponded more or less to the current Italian region of Liguria. However, this region was much larger than today's borders. To the north the boundary was the Po river in present-day Piedmont, to the west it was the Var river in the Alpes Maritimes, to the east it was the Magra river as is still the case . And to the south, the region has been bordered since the dawn of time by the Ligurian Sea. This region is therefore very mountainous including the south of the Alps and the Ligurian Apennines.
Little is known about the ancient language of the Ligurians because there are no known written records or inscriptions in it, and because it is not known where the ancient Ligurian people originally came from, an autochthonous origin is increasingly probable. This mysterious alphabet is found throughout Liguria and dates from the 6th century BC. Most of these engravings are made on steles representing warriors.[6][7] It is not known where the ancient Ligurian people originally came from, an autochthonous origin is increasingly probable. In any case, no genetic study has challenged the indigenous origin of this people. Some people have suggested that it may have been a Pre-Indo-European.[8] Some think a connection with the Celts but it is a certain anachronism given that the Celtic culture arrives very late. Moreover, there is no relationship between the Italic populations of southern Europe living in areas of relief inside the Alpine arc and the populations of Western Europe living in the plains of France. The Var river and the Alps are considered an important ethno-cultural border, where even the climate is radically different.[9][10]
Name[edit]
The name "ligure" has gone through the centuries and has never changed. The origin of this name is currently unknown and seems to predate the arrival of the Romans, Carthaginians or Greeks. The Greeks and in particular Strabo quote the Ligurians several times. When Hannibal arrived in Italy, the Ligurians participated with the Carthaginians in the battles against the Romans and these are called Ligurians. The Romans already called them ligures and the Greeks "λιγούρες" which also translates as ligures. In no ancient text is there mentioned another name to define this people.[11][9][10]
Geographical area of ancient Liguria[edit]
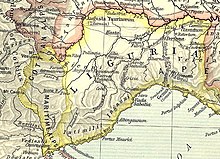
The geography of Strabo, from book 2, chapter 5, section 28 :
The Alps are inhabited by numerous nations, but all Keltic with the exception of the Ligurians, and these, though of a different race, closely resemble them in their manner of life. They inhabit that portion of the Alps which is next the Apennines (Alpes Maritimes), and also a part of the Apennines themselves (Ligurian Alps and Ligurian Apennine). This latter mountain ridge traverses the whole length of Italy from north to south, and terminates at the Strait of Sicily.[12]
— Strabo (1st century BC).
This zone corresponds to the current region of Liguria in Italy as well as to the former county of Nice which could be compared today to the Alpes Maritimes.
The writer, naturalist and Roman philosopher Pliny the Elder writes in his book "The Natural History" book III chapter 7 on the Ligurians and Liguria :
The more celebrated of the Ligurian tribes beyond the Alps are the Salluvii, the Deciates, and the Oxubii (...) The coast of Liguria extends 211 miles40, between the rivers Varus and Macra.[13]
Just like Strabo, Pliny the Elder situates Liguria between the rivers Varus and Magra. He also quotes the Ligurian peoples living on the other side of the banks of the Var and the Alps. He writes in his book "The Natural History" book III chapter 6 :
Gaul is divided from Italy by the river Varus, and by the range of the Alps (...) Forum Julii Octavanorum, a colony, which is also called Pacensis and Classica, the river Argenteus, which flows through it, the district of the Oxubii and that of the Ligauni (ligurian ethnicity). above whom are the Suetri, the Quariates and the Adunicates (celtic ethnicity). On the coast we have Antipolis, a town with Latian rights, the district of the Deciates (ligurian ethnicity), and the river Varus, which proceeds from Mount Cema, one of the Alps.[14]
So there is no archaeological evidence or ancient text that affirms the presence of Ligurians in southern Gaul except in the Alpes-Maritimes, of which the major part of this territory was in Italy until 1860. We note that Pliny the Elder cites the Ligurian peoples between the river Argenteus and Varus, which corresponds to the western part of the Alpes-Maritimes. The southern Gaul was therefore populated by Celts before the Germanic invasions of the Franks at the end of the Roman Empire. While Liguria was populated by Italic population, the Ligurians.
At that time Nice was not located in Gaul but in Italy because the sharing was done according to ethnic-cultural peoples and geography. The Var river and the Alps separated the Celtic lands and populations from the Ligurians. Nice became French very recently following the invasion of 1870. The city therefore became a French enclave in the Italian geographical zone. But the city does not change its location, it remains in the Italian geographical area. This is why one cannot say that there were Ligurians in Gaul. We can however say that Ligurians lived in the department of the Maritime Alps corresponding to this zone.
The city of Nice is not the only problem that confuses the origin of the Ligurians because it also comes from a bad interpretation of a text. The Celts living in the region between Marseille and Antibes are called the Salyes. The Greeks called them the Ligyes, or the Celts ligyans, or Kelto-Ligyes in Greek. But there is no relationship with the Ligurians. Strabo uses the word ligures to name the ligures in the same text. In this same book, he writes that the Celts and the Ligurians are of a different "race". The Ligurians are an Italic people from southern Europe. The Celts are a people of Western Europe. The Alps and the Var river separate them.
History[edit]
Proto-history of Liguria[edit]

The Copper Age arrives very early in the Italian geographical area and therefore in Liguria. Copper begins to be mined from the middle of the 4th millennium BC in Liguria with the Libiola and Monte Loreto mines dated to 3700 BC.. These are the oldest copper mines in the western Mediterranean basin.[15] It was during this period of the Copper Age in Italy that we find throughout Liguria a large number of anthropomorphic stelae in addition to rock engravings.
The bronze metallurgy (weapons, work tools, etc.) was well developed among these populations. As for the burial customs both cremation and inhumation were practiced.
The foundation of Genoa[edit]
The Genoa area has been inhabited since the fifth or fourth millennium BC.[16] In ancient times this area was inhabited by Ligures (ancient people after whom Liguria is named). According to excavations carried out in the city between 1898 and 1910, the Ligure population that lived in Genoa maintained trade relations with the Etruscans and the Greeks, since several objects from these populations were found.[17][18] In the 5th century BC the first town, or oppidum, was founded at the top of the hill today called Castello (Castle), which is now inside the medieval old town. The ancient Ligurian city was known as Stalia (Σταλìα), referred to in this way by Artemidorus Ephesius and Pomponius Mela; this toponym is possibly preserved in the name of Staglieno, some 3 km (2 mi) from the coast. Stalia had an alliance with Rome through a foedus aequum (equal pact) in the course of the Second Punic War (218-201 BC). The Carthaginians accordingly destroyed it in 209 BC. The town was rebuilt and, after the Carthaginian Wars ended in 146 BC, it received municipal rights. The original castrum then expanded towards the current areas of Santa Maria di Castello and the San Lorenzo promontory. Trade goods included skins, timber, and honey. Goods were moved to and from Genoa's hinterland, including major cities like Tortona and Piacenza. An amphitheater was also found there among other archaeological remains from the Roman period.
Western Alps and Po Valley[edit]
According to a legend, of the late Bronze Age are the foundations of Brescia and Barra (Bergamo) by Cydno, the forefather of Ligurians.[19] This myth seems to have a grain of truth, because recent archaeological excavations have unearthed remains of a settlement dating back to 1,200 B.C. that scholars presume to have been built and inhabited by Ligures peoples.[20][21] Others scholars attribute the founding of Bergamo and Brescia to the Etruscans.[22][23]
Starting from the 12th century B.C., from the union of the previous cultures of Polada and Canegrate, at the Villanova culture in central Italy, a new civilization developed that archaeologists call Golasecca from the name of the place where the first discoveries were found.
The People of Golasecca Culture inhabited a territory of about 20,000 km2, from the Alpine watershed to the Po, from Valsesia to the Serio, gravitating around three main centers: the area of Sesto Calende, Bellinzona, but especially the protourban center of Como.
The Etruscan expansion in the plain of the Po confined the Ligurians between the Alps and the Apennines, where they offered such resistance to Roman penetration that they gained a reputation with the ancients for primitive fierceness.
The Etruscan expansion[edit]

Ligurian sepulchres of the Italian Riviera and of Provence, holding cremations, exhibit Etruscan and Celtic influences.[24]
In the seventh century BC, in addition to the Greeks, the Etruscans also began to push in the northern Tyrrhenian Sea, until what is now called the Ligurian Sea.
Although they had intense commercial exchanges, they were competitors of the Greeks, with whom they often clashed. From 540 B.C. about the Etruscan presence in the Po Valley experienced a renewed expansion in the scenario following the Battle of Alalia resulted in a progressive limitation of Etruscan movements in the Upper Tyrrhenian Sea.[25] The expansion to the north of the Apennines is characterized by that moment as aimed at identifying and controlling new trade routes
Their expansionist policy was different from that of the Greeks: their expansion was mainly by land, trying gradually to occupy the areas bordering them. Even though they were good sailors, they did not found far away colonies, but at the very least emporiums destined to support trade with the local populations. This created an ambivalence in the relations with the Ligurians; on the one hand they were excellent commercial partners for all the coastal emporiums, on the other hand, their expansionist policy led them to press on the Ligurian populations settled north of the Arno river, making them retreat into the mountain areas of the northern Apennines.
Even in this case, the Ligurian opposition prevented the Etruscans from going further; indeed, although traditionally the border between the Ligurian and Etruscan areas is considered the Magra river, it is testified that the Etruscan settlements north of the Arno (for example Pisa) were periodically attacked and plundered by the Ligurian tribes of the mountains.
As already mentioned, hostility to the borders did not prevent an intense commercial relationship, as evidenced by the large quantity of Etruscan ceramics found in the Ligurian sites. Of this period is the foundation of the oppida of Genua (nowadays Genoa, about 500 BC), the urban core of the "Castello" (perhaps an ancient Ligurian oppidum) began,[26] for flourishing trade, to expand towards today's Prè (the area of meadows) and the Rivo Torbido. Some scholars believe that Genoa was an Etruscan emporium, and that only later, the local Ligurian tribe took control (or merged with the Etruscans).[27] However, the human occupation of the region of Genoa is early. The oldest traces of sedentarization found in the region of Genoa are dated from the Neolithic period to the 5th millennium BC. J.-C. Remains of more recent dwellings dating from the Bronze Age (a dry stone wall3) were also found at the mouth of the Bisagno.[28]
From that moment on, Genoa, inhabited by the Ligurian Genuati, was considered by the Greeks, given its strong commercial character, "the emporium of the Ligurians": wood for shipbuilding, livestock, leather, honey, textiles were some of the Ligurian products of commercial exchange.
The Celts on the other side of the Alps and the Var[edit]

The emergence of celtic culture appears around the middle of the 3 BC. However, nothing is known of the exchanges that there may have been between the much older Ligurian kingdoms and this new culture on the other side of the Alps and the Var.
First contacts with Romans[edit]
In the third century B.C., the Romans, having been right of the Etruscans and integrated their territories, found themselves in direct contact with the Ligurians. However, Roman expansionism was directed towards the rich territories of Gaul and the Iberian Peninsula (then under Carthaginian control), and the territory of the Ligurians was on the road (they controlled the Ligurian coasts and the South-western Alps).
At the beginning the Romans had a rather condescending attitude: the Ligurian territory was considered poor, while the fame of its warriors was known (they had already met them as mercenaries), finally they were already engaged in the First Punic War and were not willing to open new fronts, so they tried first of all to make them allies. However, despite their efforts, only a few Ligurian tribes made alliance agreements with the Romans, notably the Genuates. The rest soon proved hostile.
The hostilities were opened in 238 BC by a coalition of Ligurians and Boii Gauls, but the two peoples soon found themselves in disagreement and the military campaign came to a halt with the dissolution of the alliance. Meanwhile, a Roman fleet commanded by Quintus Fabius Maximus routed Ligurian ships on the coast (234-233 BC), allowing the Romans to control the coastal route to and from Gaul.
In 222 B.C. the Insubres, during a war with Romans occupied the oppidum of Clastidium, that at that time, it was an important locality of the Anamari (or Marici), a Ligurian tribe that, probably for fear of the nearby warlike Insubres, had already accepted the alliance with Rome the year before.
For the first time, the Roman army marched beyond the Po, expanding into Gallia Transpadana. In 222 BC, the battle of Clastidium was fought, and allowed Rome to take the capital of the Insubres, Mediolanum (modern-day Milan). To consolidate its dominion, Rome created the colonies of Placentia in the territory of the Boii and Cremona in that of the Insubres.[29]
Second Punic War[edit]
With the outbreak of the second Punic war (218 B.C.) the Ligurian tribes had different attitudes. Some, like the tribes of the west Riviera and the Apuani, allied with the Carthaginians, providing soldiers to Hannibal's troops when he arrived in Northern Italy, hoping that the Carthaginian general would free them from the neighbouring Romans. Others, like the Genuates, Bagienni and the Taurini, took sides in support of the Romans.
The pro-Carthaginian Ligurians took part in the Battle of the Trebia, which the Carthaginians won. Other Ligurians enlisted in the army of Hasdrubal Barca, when he arrived in Cisalpine Gaul (207 BC), in an attempt to rejoin the troops of his brother Hannibal. In the port of Savo (modern-day Savona), then capital of the Ligures Sabazi, triremes of the Carthaginian fleet of Mago Barca, brother of Hannibal, which were intended to cut the Roman trade routes in the Tyrrhenian Sea, found shelter.
In the early stages of the war, the pro-Roman Ligurians suffered. The Taurini were on the path of Hannibal's march into Italy, and in 218 BC, they were attacked by him, as he had allied with their long-standing enemies, the Insubres. The Taurini chief town of Taurasia (modern-day Turin) was captured by Hannibal's forces after a three-day siege.[30]
In 205 BC, Genua (modern-day Genoa) was attacked and razed to the ground by Mago.[31]
Near the end of the Second Punic War, Mago was among the Ingauni, trying to block the Roman advance. At the Battle of Insubria, he suffered a defeat, and later, died of wounds sustained in the battle. Genua was rebuilt in the same year.
Ligurian troops were present at the Battle of Zama in 202 BC, which marked the final end of Carthage as a great power.[32]
Roman conquest of Ligurians[edit]

In 200 BC, the Ligures and Boii sacked and destroyed the Roman colony of Placentia, effectively controlling the most important ford of the Po Valley.[33]
During the same period, the Romans were at war with the Apuani. Serious Roman efforts began in 182, when both consular armies and a proconsular army were sent against the Ligurians. The wars continued into the 150s, when victorious generals celebrated two triumphs over the Ligurians. Here too, the Romans drove many natives off their land and settled colonies in their stead (e.g., Luna and Luca in the 170s). During the same period, the Romans were at war with the Ligurian tribes of the northern Apennines.
By the end of the Second Punic War, however, hostilities were not over yet. Ligurian tribes and Carthaginian holdouts operating from the mountain territories continued to fight with guerrilla tactics. Thus, the Romans were forced into continuous military operations in northern Italy.
In 201 BC, the Ingauni signed a peace treaty with Rome.
It was only in 197 BC that the Romans, under the leadership of Minucius Rufus, succeeded in regaining control of the Placentia area by subduing the Celelates, Cerdicates, Ilvati and the Boii Gauls and occupying the oppidum of Clastidium.
Genua was rebuilt by the proconsul Spurius Lucretius in the same year. Having defeated Carthage, Rome sought to expand northwards, and used Genua as a support base for raids, between 191 and 154 BC, against the Ligurian tribes of the hinterland, allied for decades with Carthage.
A second phase of the conflict followed (197-155 BC), characterized by the fact that the Apuani Ligurians entrenched themselves on the Apennines, from where they periodically descended to plunder the surrounding territories. The Romans, for their part, organized continuous expeditions to the mountains, hoping to snide, surround and defeat the Ligurians (taking care not to be destroyed by ambushes). In the course of these wars, the Romans celebrated fifteen triumphs and at suffered at least one serious defeat.
Historically, the beginning of the campaign dates back to 193 BC on the initiative of the Ligurian conciliabula (federations), who organized a major raid going as far as the right bank of the river Arno. Roman campaigns followed (191, 188 and 187 BC); these were victorious, but not decisive.
In the campaign of 186 BC, the Romans were beaten by the Ligurians in the Magra valley. In this battle, which took place in a narrow and precipitous place, the Romans lost about 4000 soldiers, three eagle insignia of the second legion and eleven banners of the Latin allies. In addition, the consul Quintus Martius was also killed in the battle. It is thought that the place of the battle and the death of the consul gave rise to the place-name of Marciaso, or that of the Canal of March on Mount Caprione in the town of Lerici (near the ruins of the city of Luni), which was later founded by the Romans. This mountain had a strategic importance because it controlled the valley of Magra and the sea.
In 185 BC, the Ingauni and the Intimilii also rebelled and managed to resist the Roman legions for the next five years, before capitulating in 180 BC. The Apuani, and those of hinterland side still resisted.
However, the Romans wanted to permanently pacify Liguria to facilitate further conquests in Gaul. To that end, they prepared a large army of almost 36,000 soldiers, under the command of proconsuls Publius Cornelius Cethegus and Marcus Baebius Tamphilus, with the aim of putting an end to Ligurian independence.
In 180 BC, the Romans inflicted a serious defeat on the Apuani Ligures, and deported 40,000 of them to the regions of Samnium. This deportation was followed by another one of 7,000 Ligurians in the following year. These were one of the few cases in which the Romans deported defeated populations in such a high number. In 177 BC other groups of Apuani Ligures surrendered to the Roman forces, and were eventually assimilated into Roman culture during the 2nd century BC, while the military campaign continued further north.[34]
The surviving Ligurian tribes, now isolated and in absolute inferiority, continued to fight.
The Frinatiates surrendered in 175 BC, followed by the Statielli (172 BC) and the Velleiates (158 BC). The last Apuani resistance was subdued in 155 BC by consul Marcus Claudius Marcellus.
Subjugation of "transalpine" and "Capillati" Ligures[edit]
The subjugation of the coastal Ligures and the annexation of the Alpes Maritimae took place in 14 BC, closely following the occupation of the central Alps in 15 BC.[35]
The last Ligurian tribes (e.g. Vocontii and Salluvii) still autonomous, who occupied Provence, were subdued in 124 BC.[36]
Under Roman rule[edit]
The Padania[edit]
The Cisalpine Gaul was the part of modern Italy inhabited by Celts during the 4th and 3rd centuries BC. Conquered by the Roman Republic in the 220s BC, it was a Roman province from c. 81 BC until 42 BC, when it was merged into Roman Italy as indicated in Caesar's will (Acta Caesaris).[37][38]
Northern Italy was further subdivided into Regio VIII Aemilia, Regio IX Liguria, Regio X Venetia et Istria and Regio XI Transpadana, i.e. its portions south and north of the Po River, respectively. The Roman province of the 1st century BC was bounded on the north and west by the Alps, in the south as far as Placentia by the river Po, and then by the Apennines and the river Rubicon, and in the east by the Adriatic Sea.[39] In 49 BC all inhabitants of Padania (northern italy) received Roman citizenship.[40]
The Regio IX Liguria[edit]

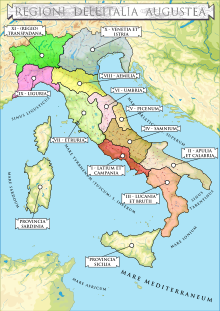
Around 7 BC, Augustus divided Italy into eleven regiones, as reported by Pliny the Elder in his Naturalis Historia. Northern Italy was divided among four of the eleven regions of Italy: Regio VIII Aemilia, Regio IX Liguria, Regio X Venetia et Istria and Regio XI Transpadana (on the other side of the mythical Po river).[41] One of this was The Regio IX Liguria, in 6 A.D. Genoa became the centre of this region and the Ligurian populations moved towards the definitive Romanisation.
The official historical name did not have the Liguria apposition, due to the contemporary academic use of naming the Augustan regions according to the populations they understood. Royal IX included only the Ligurian territory. This territory extended from the Maritime and Cottian Alps and the Var river (to the west) to the Trebbia and the Magra bordering Regio VIII Aemilia and Regio VII Etruria (to the east), and the Po to North.[42]
The description of the IX regio Italiae goes back to Pliny:[43] "patet ora Liguriae inter amnes Varum et Macram XXXI Milia passuum. Haec regio ex descriptione Augusti nona est".

People with Ligurian names were living south of Placentia, in Italy, as late as 102 AD.[44]
In 126 A.D. the Liguria region was the birthplace of Pertinax, Roman soldier and politician who became Roman Emperor.
The Kingdom of Cottius[edit]

The area of the Alpes Cottiae province, named after Cottiust, the local king of Ligurian tribe of Segusini, who initially resisted Augustus' imperialism but eventually submitted and became the emperor's ally and personal friend. His territory, together with that of the other Alpine tribes, was annexed to the Roman empire in 15 BC - although Cottius, and his son after him, were accorded the unusual privilege of continuing to govern the region, with the title of praefectus i.e. Roman governor.[45] In 8 BC, Cottius showed his gratitude for this reprieve from dynastic oblivion by erecting a triumphal arch to Augustus in his capital, Segusio (Susa, Piedmont, Italy), which still stands. After the death of Cottius' son, the emperor Nero (ruled 54-68) appointed a regular equestrian procurator to govern the province.[46]
Ancient source[edit]
Thucydides also speaks of the Ligures having expelled the Sicanians, an Iberian tribe, from the banks of the river Sicanus, in Iberia.[47]
French theories concerning the origin of the Ligurians[edit]

In the 19th century, the origins of the Ligures drew renewed attention from scholars. Amédée Thierry, a French historian and journalist, linked them to the Iberians.[48] The historian of the Bourgogne and specialist in its Gallic culture, Dominique-François-Louis Roget, Baron de Belloguet, would later claim a "Gallic" origin of the Ligurians.[49] During the Iron Age the spoken language, the main divinities and the workmanship of the artifacts unearthed in the area of Liguria (such as the numerous torcs found) were similar to those of Celtic culture in both style and type.[50]
Karl Müllenhoff, professor of Germanic antiquities at the Universities of Kiel and Berlin, studying the sources of the Ora maritima by Avienius (a Latin poet who lived in the 4th century AD, but who used as a source for his own work a Phoenician Periplum of the 6th century BC),[51] held that the name 'Ligurians' generically referred to various peoples who lived in Western Europe, including the Celts, but thought the "real Ligurians" were a Pre-Indo-European population.[52] Italian geologist and paleontologist Arturo Issel considered Ligurians to be direct descendants of the Cro-Magnon people that lived throughout Gaul from the Mesolithic period.[53]
Those in favor of an Indo-European origin included Henri d'Arbois de Jubainville, a 19th-century French historian, who argued in Les Premiers habitants de l'Europe (1877) that the Ligurians were the earliest Indo-European speakers of Western Europe. Jubainville's "Celto-Ligurian hypothesis", as it later became known, was significantly expanded in the second edition of his initial study. It inspired a body of contemporary philological research, as well as some archaeological work. The Celto-Ligurian hypothesis became associated with the Funnelbeaker culture and "expanded to cover much of Central Europe".[54]
Julius Pokorny adapted the Celto-Ligurian hypothesis into one linking the Ligures to the Illyrians, citing an array of similar evidence from Eastern Europe. Under this theory the "Ligures-Illyrians" became associated with the prehistoric Urnfield peoples.[55]
Today some accounts suggest that the Ligures represented the northern branch of an ethno-linguistic layer older than and very different from the proto-Italic peoples. It was believed that a "Ligurian-Sicanian" culture occupied a wide area of southern Europe,[56] stretching from Liguria to Sicily and Iberia. However, while any such area would be broadly similar to that of the paleo-European "Tyrrhenian culture" hypothesized by later modern scholars, there are no known links between the Tyrrenians and Ligurians.
There are others such as Dominique Garcia, who question whether the Ligures can be considered a distinct ethnic group or culture from the surrounding cultures.[57][58]
Culture[edit]
Language[edit]

The ancient name of Po river (Padus in Latin) derived from the Ligurian name of the river:[59] Bod-encus or Bod-incus. This word appears in the place name Bodincomagus, a Ligurian town on the right bank of the Po downstream near today's Turin.[60]
Society[edit]

The Ligurians never formed a centralized state, they were in fact divided into independent tribes, in turn organized in small villages or castles. Rare were the oppidas, to which corresponded the federal capitals of the individual tribes or important commercial emporiums.
The territory of a tribe was almost entirely public property, only a small percentage of the land (the cultivated) was "private", in the sense that, against payment of a small tax, was given in concession. Only late in life did the concept of private, heritable or marketable property develop.
Reflecting the decentralized character of the ethnic group, the Ligurians did not have a centralized political structure. Each tribe decided for itself, even in contrast with the other tribes; as evidence of this, are the opposing alliances that over time Ligurian tribes made against Greeks, Etruscans and Romans.
Within the tribes, an egalitarian and communal spirit prevailed. If there was also a noble class, this was tempered by "tribal rallies" in which all the classes participated; there does not seem to have been any pre-organized magistracy. There were no dynastic leaders either: the Ligurian "king" was elected as leader of a tribe or a federation of tribes; only in late period did a real dynastic aristocratic class begin to emerge. Originally there was no slavery: prisoners of war were massacred or sacrificed.[61]
Diodorus Siculus, in the first century B.C., writes that women take part in the work of toil alongside men.[62]
Religion[edit]
De Bello Civili (On the Civil War), more commonly referred to as the Pharsalia, is a Roman epic poem written by the poet Lucan, from book 1, card 5 :
Ligurian tribes, now shorn, in ancient days
First of the long-haired nations, on whose necks Once flowed the auburn locks in pride supreme; And those who pacify with blood accursed Savage Teutates, Hesus' horrid shrines, And Taranis' altars, cruel as were those Loved by Diana, goddess of the north; All these now rest in peace. And you, ye Bards, Whose martial lays send down to distant times The fame of valorous deeds in battle done, Pour forth in safety more abundant song. While you, ye Druids, when the war was done, To mysteries strange and hateful rites returned: To you alone 'tis given the heavenly gods To know or not to know; secluded groves Your dwelling-place, and forests far remote. If what ye sing be true, the shades of men Seek not the dismal homes of Erebus Or death's pale kingdoms; but the breath of life Still rules these bodies in another age- Life on this hand and that, and death between. Happy the peoples 'neath the Northern Star In this their false belief; for them no fear Of that which frights all others: they with hands And hearts undaunted rush upon the foe
And scorn to spare the life that shall return.[3]
— Lucan (1st century AD).
Among the most important testimonies, the sacred mountain sites (Mont Bègo, Monte Beigua) and the development of megalithicism (statues-stelae of Lunigiana) are worth mentioning.
The spectacular Mont Bégo in Vallée des merveilles is the most representative site of the numerous sacred sites covered with rock carvings, and in particular with cupels, gullies and ritual basins. The latter would indicate that a fundamental part of the rites of the ancient Ligurians, provided for the use of water (or milk, blood?). The site of Mont Bégo has an extension and spectacularity comparable to the sites of Val Camonica. Another important sacred centre is Mount Beigua, but the reality is that many promontories in North-west Italy and the Alps present these types of sacred centres.
Among the more considerable Ligurian monuments are rock engravings and anthropomorphic sculptures analogous to those of southern France, found in Lunigiana and Corsica. Some of these artistic manifestations are repeated in territories farther east[24]
The other important evidence is the proliferation of megalithic events, the most spectacular and original of which is that of the stele statues in the Lunigiana. These particular oblong stones, stuck in the ground of the woods, ended with stylized human heads, and could be equipped with arms, sexual attributes and significant objects (e.g. daggers). Their real meaning has been lost in memory, today it is assumed that they represented:
- gods;
- ancestors and divinized heroes;
- the birth from the womb to symbolize the origin of their race originated directly from the womb of the earth and nature.
The heads, so represented, for the Ligurians were the seat of the soul, the center of emotions and the point of the body where all the senses were concentrated, consequently the essence of the divine and hence its cult.

In general, it is believed that the Ligurian religion was rather primitive, addressed to supernatural tutelary gods, representing the great forces of nature, and from which you could get help and protection through their divination.
The proliferation of sacred centers near the peaks, would indicate the cult of majestic celestial numes, represented by the high peaks: in fact Beg- (from which Baginus and Baginatie), Penn- (later transformed by Romanization in Iuppiter Poeninus and in the Apenninus pater) and Alb- (from which Albiorix) are indicated as tutelary numes of the Ligurian peaks.
Numbers such as Belenus and Borvo, linked to the cult of water, and the cult of Matronae (hence the sanctuary of Mons Matrona, now Montgenèvre) are also mentioned.
Among the many engravings, significant is the presence of the figure of the bull, even if only stylized through the symbol of the horns, this would indicate the cult of a deity taurine, male and fertilizer, already known to Anatolian and Semitic cultures.
Another important deity was Cycnus of Liguria, which perhaps represents the divinization of a mythical ancient king or, the totemic animal associated with the cult of the sun.
Clothing[edit]
Diodorus Siculus reports the use of a tunic tightened at the waist by a leather belt and closed by a clasp generally bronze; the legs were naked.[63] Other garments used were cloaks "sagum", and during the winter animal skins to shelter from the cold.[64] Characteristic element was the fibula, used to close the clothes and the cloaks, made of amber (imported from the Baltic) and glass paste, enriched with ornamental elements in bone or stone.
Physical appearance[edit]
Lucan in his Pharsalia (c. 61 AD) described Ligurian tribes as being long-haired, and their hair a shade of auburn (a reddish-brown):
...Ligurian tribes, now shorn, in ancient days
First of the long-haired nations, on whose necks
Once flowed the auburn locks in pride supreme.[65]
Warfare[edit]

Diodorus Siculus describes the Ligurians as very fearsome enemies: although not particularly impressive from the physical point of view, strength, will and tenacity makes them the most dangerous warriors than the gauls. As proof of this, the Ligurian warriors were very much in demand as mercenaries and several times the Mediterranean powers like Carthage and Syracuse, went to Liguria to recruit armies for their expeditions (for example, the elite troops of Hannibal were made up of a contingent of Ligurians).[citation needed]
Tactics, unit types and equipment[edit]
The armament varied according to the class and the comfort of the owner, in general however the great mass of the Ligurian warriors was substantially light infantry, armed in a poor way[64][66] The main weapon was the spear, with cusps that could exceed a cubit (about 45 cm, or one and half foot ), followed by the sword, of Gallic shape (sometimes cheap because made with soft metals), very rarely the warriors were equipped with bows and arrows.
The protection was entrusted to an oblong shield of wood,[67] always of Celtic typology (but to difference of this last one without metallic boss)[68] and a simple helmet, of Montefortino type.
The horned helmets, recovered in the Apuani tribe area, were probably used only for ceremonial purpose and they were worn by warchief, to underline their virility and military skills. The use of armor is not known: the seated warrior from the site of Roquepertuse seems to wears a leather armor, although the statue is attributable to the 5th century A.D. and the armor maybe was used only in this period. Even if it is possible that the richer warriors used armor in organic material like the Gauls[68] or the Greek linothorax .[69]
The infantry was good both close combat as skirmishes but could fight hand-to-hand when necessary.
Cavalry[edit]

Strabo and Diodorus Siculus say they fought almost on foot, because of the nature of their territory, but their phrasing implies that cavalry were not entirely unknown, and two recently discovered Ligurian graves have included harness fittings. Strabo says that the Salyes tribe located north of Massalia, have a substantial cavalry force, but, they were one of the several Celto-Ligurian tribes, and probably the cavalry reflect the Celtic element [63]

Mercenaries[edit]
The Ligures seem to have been ready to engage as mercenary troops in the service of others. Ligurian auxiliaries are mentioned in the army of the Carthaginian general Hamilcar I in 480 BC.[70] Greek leaders in Sicily continued to recruit Ligurian mercenary forces from the same quarter as late as the time of Agathocles.[47][71]
The mercenary trade was a particular form of trade and income: as the Greek and Roman sources attest, from very ancient times the Ligurians served as mercenaries in the armies of the western Mediterranean. The enlistment took place by contingents (obviously not for individual soldiers), as it was essential to have well-functioning units. Centuries of war experiences in the wars between Etruscans, Carthaginians, provided the Ligurians with war skills such as to keep the Roman armies in check for several decades.
Piracy[edit]
In ancient times, a side activity to the seafaring was piracy, and the Ligurians were no exception. If they thought it was appropriate, they attacked and plundered ships sailing along the coast. The thing is not surprising: even in ancient times the fastest way to obtain goods is to steal them. After all, the continuous raids of the Ligurian tribes in the territories of the neighbouring peoples are well documented, and constitute an important voice in their economy. The Ingauni, a tribe of sailors located around Albingaunum (nowadays Albenga) were famous to engage trade and piracy, hostiles to Rome,[72] they were subdued by consul Lucius Emilius Paullus Macedonicus in 181 BC.[73]
Under Roman service[edit]
After the Roman conquest, in the 171-168 some of them combated with the Romans against Macedonia, by the time of Gaius Marius they became commoner in Roman army.
According to Plutarch the Battle of Pydna, the decisive battle of Third Macedonian War, started in the afternoon, for an artifice devised by Roman consul L.Emillius Paullus. In order to make the enemies move in battle first, he pushed before a horse without reins the Romans threw him against them, and the pursuit of the horse began the attack. According to another theory instead, the Thracians in Macedonian service, attacked some Roman foragers getting a little too close to enemy lines, and in response there was the immediate charge of 700 Ligurian auxiliaries.[74]
Before Pydna the Romans used their Ligurian auxiliares with the velites for chasing off the Macedonian skirmishers (the peltasts)[63]
Sallustius and Plutarch say that during the Jugurthine War (from 112 to 105 BC)[75] and the Cimbrian War (from 104 to 101 BC)[76] the Ligurians served as auxiliary troops in the Roman army. In the course of this last conflict they played an important role in the Battle of Aquae Sextae.
Ligures in its broad sense included all the Ligurian peoples of north western Italy, between the Var and Magra rivers, in the apennines and the southern alps, however because Regio Liguria was annexed to Italia, the inhabitants of this region became Roman citizens, and would have been recruited into the legions.
Economy[edit]
The Ligurian economy was based on primitive agriculture, sheep farming, hunting and the exploitation of forests. Diodorus Siculus writes about the Ligurians:
"Since their country is mountainous and full of trees, some of them use all day to cut wood, using strong and heavy dark; others, who want to cultivate the land, must deal with breaking stones, because it is so dry soil that you can not pick tools remove a sod, that with it do not rise stones. However, even if they have to fight with so many misfortunes, by means of stubborn work they go beyond nature [...] they often give themselves to hunting, and finding quantities of savage, with it they make up for the lack of bladders; and so it comes, that flowing through their snow-covered mountains, and getting used to practicing then more difficult places of the thickets, they harden their bodies, and strengthen their muscles admirably. Some of them, due to the famine of food, drink water, and live of meat of domestic and wild animals.[77]
Thanks to the contact with the bronze "metal seekers", the Ligurians also dedicated themselves to the extraction of minerals[78] and metallurgy, even if most of the metal in circulation is of central European origin.
The commercial activity is important. Already in ancient times the Ligurians were known in the Mediterranean for the trade of the precious Baltic amber. With the development of the Celtic populations, the Ligurians found themselves controlling a crucial access to the sea, becoming (sometimes in spite of themselves) custodians of an important way of communication.
Although they were not renowned navigators, they came to have a small maritime fleet, and their attitude to navigation is described as follows:
"They sail for reason of shops on the sea of Sardinia and Libya, spontaneously exposing themselves to extreme dangers; they use smaller hulls than vulgar boats for this; nor are they practical of the comfort of other ships; and what is surprising is that they are not afraid to sustain the serious risks of storms.[77]
Tribes[edit]
See also[edit]
- List of ancient Ligurian tribes
- Ancient peoples of Italy
- Mont Bègo
- Golasecca Culture
- Cisalpine Gaul
- Torrean civilization
References[edit]
- ^ "Vitruvius Pollio, the Ten Books on Architecture, BOOK VIII, CHAPTER III: VARIOUS PROPERTIES OF DIFFERENT WATERS".
- ^ "C. Suetonius Tranquillus, Tiberius, chapter 37".
- ^ a b "M. Annaeus Lucanus, Pharsalia, book 1, line 396".
- ^ "C. Suetonius Tranquillus, Nero, chapter 18".
- ^ Maggiani, Adriano (2004). "Popoli e culture dell'Italia preromana. I Liguri". Il Mondo dell'Archeologia (in Italian). Rome: Treccani editore. Retrieved September 14, 2019.
Alla relativa abbondanza delle fonti letterarie circa queste popolazioni, che una parte della critica storiografica di tradizione ottocentesca voleva estese dal Magra all'Ebro, non corrisponde un panorama archeologico altrettanto ricco, che anzi, anche all'interno della Liguria storica, è ben lungi dal presentare caratteri unitari.
- ^ "Sulle pietre dell'Appennino l'antica cultura dei Liguri". 18 June 2019.
- ^ Tintorri, Ivan; Adolfo, Zavaroni. "Pietre Con Scritte e Figure dei Liguri Friniati Alle Caselle di Ospitale (Appennino Modenese)".
- ^ "Liguri". Enciclopedie on line. Treccani.it (in Italian). Rome: Treccani -Istituto dell'Enciclopedia Italiana. 2011.
Le documentazioni sulla lingua dei Liguri non ne permettono una classificazione linguistica certa (preindoeuropeo di tipo mediterraneo? Indoeuropeo di tipo celtico?).
- ^ a b "Strabo, Geography, BOOK II., CHAPTER V., section 28".
- ^ a b "Pliny the Elder, the Natural History, BOOK III. AN ACCOUNT OF COUNTRIES, NATIONS, SEAS, TOWNS, HAVENS, MOUNTAINS, RIVERS, DISTANCES, AND PEOPLES WHO NOW EXIST OR FORMERLY EXISTED., CHAP. 7.—OF THE NINTH1 REGION OF ITALY. 1 Italy was divided by Augustus into eleven districts; the ninth of which nearly corresponded to the former republic of Genoa".
- ^ "Perseus Digital Library".
- ^ "Strabo, Geography, BOOK II., CHAPTER V., section 28". www.perseus.tufts.edu.
- ^ "Pliny the Elder, the Natural History, BOOK III. AN ACCOUNT OF COUNTRIES, NATIONS, SEAS, TOWNS, HAVENS, MOUNTAINS, RIVERS, DISTANCES, AND PEOPLES WHO NOW EXIST OR FORMERLY EXISTED., CHAP. 7.—OF THE NINTH1 REGION OF ITALY. 1 Italy was divided by Augustus into eleven districts; the ninth of which nearly corresponded to the former republic of Genoa".
- ^ "Pliny the Elder, the Natural History, BOOK III. AN ACCOUNT OF COUNTRIES, NATIONS, SEAS, TOWNS, HAVENS, MOUNTAINS, RIVERS, DISTANCES, AND PEOPLES WHO NOW EXIST OR FORMERLY EXISTED., CHAP. 5. (4.)—OF THE PROVINCE OF GALLIA NARBONENSIS".
- ^ https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Monte-Loreto-Fourth-millennium-cal-BC-mineshaft-ML6_fig1_265409510
- ^ The objects found during the works for the underground had been exposed in the exhibition Archeologia Metropolitana. Piazza Brignole e Acquasola, held at the Ligurian Archeology Museum (30 November 2009 - 14 February 2010) ([1] Archived December 30, 2013, at the Wayback Machine)
- ^ Melli, Piera (2007). Genova preromana. Città portuale del Mediterraneo tra il VII e il III secolo a.C. (in Italian). Frilli. ISBN 978-8875633363.
- ^ Marco Milanese, Scavi nell'oppidum preromano di Genova, L'Erma di Bretschneider, Roma 1987 on-line in GoogleBooks; Piera Melli, Una città portuale del Mediterraneo tra il VII e il III secolo a.C., Genova, Fratelli Frilli ed., 2007.
- ^ "Ducato di Piazza Pontida". www.ducatodipiazzapontida.it.
- ^ "History of Brescia: the origins and the Roman Brescia". turismobrescia.it. Retrieved 2014-06-20.
- ^ "Storia del Colle Cidneo" [History of the Cidneo Hill]. bresciamusei.com (in Italian). Retrieved 2014-05-14.
- ^ "Ducato di Piazza Pontida". www.ducatodipiazzapontida.it. Retrieved 2019-12-08.
- ^ "Le origini". www.bresciastory.it. Brescia Story. Archived from the original on 7 March 2008. Retrieved 9 December 2019.
- ^ a b Ancient Italic people, The Ligurians, Enciclopedia Britannica https://www.britannica.com/topic/ancient-Italic-people/Other-Italic-peoples#ref63581
- ^ La Battaglia del mare Sardo (540 a.C.) Archiviato il 26 febbraio 2013 in Internet Archive..
- ^ Marco Milanese, Scavi nell'oppidum preromano di Genova, L'Erma di Bretschneider, Roma 1987 testo on-line su GoogleBooks; Piera Melli , Una città portuale del Mediterraneo tra il VII e il III secolo a.C.", Genova, Fratelli Frilli ed., 2007.
- ^ Piera Melli , Una città portuale del Mediterraneo tra il VII e il III secolo a.C.", Genoa, Fratelli Frilli ed., 2007 (on-line text of the first chapter Archived on 28 February 2009 in the Internet Archive.). A marble funerary stele dedicated to Apollonia, found reused in the walls of the twelfth century was considered a proof of the Greek origin of the city: the stele, a work of the first half of the third century BC, must be considered rather arrived in Genoa along with many ancient artifacts in the Middle Ages.
- ^ "Archeologia Metropolitana Museo di Archeologia Ligure Genova". Retrieved 2022-09-28 – via Archive.wikiwix.com.
- ^ Demandt, p. 86
- ^ Polybius iii. 60, 8
- ^ Titus Livius, Ab Urbe Condita libri CXLII 21, 32,1 and 28, 46,7.
- ^ Polibius, Stories, XV, 11.1
- ^ "Ancient Rome - Roman expansion in the western Mediterranean".
- ^ Broadhead, William (2002). Internal migration and the transformation of Republican Italy (PDF) (Ph.D.). University College London. p. 15.
- ^ Dio LIV.22.3-4
- ^ Plinius the elder, Naturalis Historia, III, 47.
- ^ Williams, J. H. C. (2001). Beyond the Rubicon: Romans and Gauls in Republican Italy. ISBN 9780198153009. Archived from the original on 2020-05-22.
- ^ Long, George (1866). Decline of the Roman republic: Volume 2. London.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Schmitz, Leonhard (1857). A manual of ancient geography. Philadelphia: Blanchard and Lea.
- ^ Cassius Dio XLI, 36.
- ^ Brouwer, Hendrik H. J. (1989). Hiera Kala: Images of animal sacrifice in archaic and classical Greece. Utrecht.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Strabo, Geography, V, 1,1 and 2.1.
- ^ Plinius the Elder, Naturalis Historia, III, 49.
- ^ Boardman, John (1988). The Cambridge ancient history: Persia, Greece and the Western Mediterranean c. 525–479 BC. p. 716.
- ^ CAH X 170
- ^ 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica Segusio
- ^ a b William Smith, ed. (1854). "Liguria". Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography.
- ^ Amédée Thierry, Histoire des Gaulois depuis les temps les plus reculés, 3 vols., 1828, 1834, 1845.
- ^ Dominique François Louis Roget de Belloguet, Ethnogénie gauloise, ou Mémoires critiques sur l'origine et la parenté des Cimmériens, des Cimbres, des Ombres, des Belges, des Ligures et des anciens Celtes. Troisiéme partie: Preuves intellectuelles. Le génie gaulois, Paris 1868.
- ^ Gilberto Oneto Paesaggio e architettura delle regioni padano-alpine dalle origini alla fine del primo millennio, Priuli e Verlucc, editori 2002, pp. 34–36, 49.
- ^ Postumius Rufius Festus (qui est) Avienius, Ora maritima, 129–133 (indicating in an obscure way that the Ligures were living north of the "oestrymnic islands", equivalent to modern Portugal and Galicia); 205 (Ligures north of the city of Ophiussa [= again Portugal] in the Iberian peninsula); 284–285 (the stream Tartessus in southern Spain would be born in the "ligustine swamps").
- ^ Karl Viktor Müllenhoff, Deutsche Alterthumskunde, Vol. I: Die Phoenizier. Pytheas von Massalia, 1870.
- ^ Arturo Issel, Liguria geologica e preistorica, Vol. II, Genoa 1892, pp. 356–357.
- ^ See, in particular McEvedy, Colin (1967). The Penguin Atlas of Ancient History by Colin McEvedy. p. 29.
- ^ Henning, Andersen (2003). Language Contacts in Prehistory: Studies in Stratigraphy. John Benjamins Publishing. pp. 16–17.
- ^ Sciarretta, Antonio (2010). Toponomastica d'Italia. Nomi di luoghi, storie di popoli antichi. Milano: Mursia. pp. 174–194. ISBN 978-88-425-4017-5.
- ^ Garcia, Dominique (2012). From the Pillars of Hercules to the Footsteps of the Argonauts (Colloquia Antiqua). Peeters.
- ^ Haeussler, Ralph (2013). Becoming Roman?: Diverging Identities and Experiences in Ancient Northwest Italy. Routledge. p. 87. ISBN 9781315433202.
- ^ Daiches, David; Anthony Thorlby (1972). Literature and western civilization (illustrated ed.). Aldus. p. 78.
- ^ Cfr. la voce fossa in Alberto Nocentini, l'Etimologico. Dizionario etimologico della lingua italiana, Firenze, Le Monnier, 2010. ISBN 978-88-0020-781-2.
- ^ Livius mentions the fate of the population of Mutina, once it fell into the hands of the Ligures.
- ^ Diodorus Siculus, Bibliotheca historica, V, 39, 1.
- ^ a b c Armies of the Macedonian and Punic Wars, Duncan Head, 2012 Page 296 <https://books.google.it/books?id=-7n8CwAAQBAJ&pg=PA294&lpg=PA294&dq=ligures+warrior&source=bl&ots=1gcz-CPca-&sig=ACfU3U2IWz3f6FlupTDzRSNtwjrDZQvaRg&hl=it&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjF9dWTpurlAhUDKewKHfQvA1YQ6AEwBnoECAkQAQ#v=onepage&q=ligures%20warrior&f=false>
- ^ a b Diodorus Siculus, Bibliotheca historica, V, 39, 1-8.
- ^ Lucan, Pharsalia, I. 496, translated by Edward Ridley (1896).
- ^ Livius XXXIX I, 6
- ^ Polibius XXIX 14, 4
- ^ a b "AD PUGNAM PARATI: Rievocazione Storica, Spettacolo, Sperimentazione" (in Italian). Retrieved 2019-09-09.
- ^ The commercial contacts with the Greeks and the militancy of Ligurian mercenaries in the ranks of the Greek and Carthaginian armies of the western Mediterranean, who effectively used this type of protection, may have led to their adoption by the Ligurians.
- ^ Herodotus 7.165; Diodorus Siculus 11.1.
- ^ Diodorus Siculus 21.3.
- ^ They were on Carthaginian side during the Second Punic War also.
- ^ "Ingauni" on Enciclopedia Treccani http://www.treccani.it/enciclopedia/ingauni
- ^ Plutarch, The Lives of Emilius Paul and Timoleon XVIII
- ^ Salustio, Giugurtine War (In French)
- ^ Plutarch, Marius, 20
- ^ a b (Diodorus Siculus, in Luca Ponte, Le genovesi)
- ^ Examples of mining activities are witnessed in the Labiola mine.
Bibliography[edit]
- ARSLAN E. A. 2004b, LVI.14 Garlasco, in I Liguri. Un antico popolo europeo tra Alpi e Mediterraneo, Catalogo della Mostra (Genova, 23.10.2004-23.1.2005), Milano-Ginevra, pp. 429–431.
- ARSLAN E. A. 2004 c.s., Liguri e Galli in Lomellina, in I Liguri. Un antico popolo europeo tra Alpi e Mediterraneo, Saggi Mostra (Genova, 23.10.2004–23.1.2005).
- Raffaele De Marinis, Giuseppina Spadea (a cura di), Ancora sui Liguri. Un antico popolo europeo tra Alpi e Mediterraneo, De Ferrari editore, Genova 2007 (scheda sul volume).
- John Patterson, Sanniti,Liguri e Romani,Comune di Circello;Benevento
- Giuseppina Spadea (a cura di), I Liguri. Un antico popolo europeo tra Alpi e Mediterraneo" (catalogo mostra, Genova 2004–2005), Skira editore, Genova 2004
Further reading[edit]
- Berthelot, André. "LES LIGURES." Revue Archéologique 2 (1933): 245-303. www.jstor.org/stable/41750896.
- Ligures
- Indo-European peoples
- History of Italy
- Ancient history of France
- History of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur
- History of Piedmont
- History of Europe
- History of Liguria
- History of Lombardy
- Historical Celtic peoples
- Transhumant ethnic groups
- Ancient peoples of Italy
- Ancient peoples of France
- Ancient peoples of Spain
- Ancient peoples of Sardinia
- Ancient peoples of Europe
